- P73-04755
- Windows Server Hardware
- Learning Windows Server 2008 R2
- Windows Server 2008 Web Edition
- Windows Server 2008 Learning Pdf
- Windows Web Server 2008 R2
NetCom Learning is a reputed training partner that has been serving learners across the US and abroad for almost the past 3 decades. You can begin your learning of Windows Server with NetCom. Windows Server 2008 R2 is a network operating system Microsoft, and can be deployed in medium to large scale industries in order to allow administrators to centrally manage the entire network setup right from a single location. The main difference between a client operating system, such as Microsoft.
We are beginning to close in on the one-year mark since the release of Windows Server 2008, and more and more companies...
in 2009 are starting to plan migrations to Microsoft's latest server operating system. Although much has been said about Windows Server 2008's roles and features over the past year, those who have yet to start working with the OS might still be curious about what it has to offer.
But where to start? Don't worry -- SearchWindowsServer.com has done all the legwork for you, compiling a wealth of information on Windows 2008 since before it was released. This Windows 2008 guide features tips, videos and more covering the top features and improvements included with the OS, as well as info to help you plan your migration.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
- Getting started with Windows Server 2008
- Planning your Windows 2008 migration
- Key Windows 2008 features and improvements
- Changes to Active Directory
- Virtualization with Hyper-V
- Windows Server 2008 security considerations
- Storage improvements with Windows 2008
- Inside Windows Server 2008 R2
GETTING STARTED WITH WINDOWS SERVER 2008
Windows Server 2008 includes a lot of new features; but not all of them may be right for your organization. This section offers a crash course on the key benefits of Windows 2008, along with some of the issues administrators could run into after it's deployed.
Making the business decision to move to Windows Server 2008
Before your Windows Server 2008 migration, you should take the time understand all the features that can save your company time and money. This two-part article breaks down the business values of several Windows 2008 benefits, such as Microsoft's product support lifecycle, and features including Server Core and the read-only domain controller.
What's there to hate about Windows Server 2008?
While Microsoft's latest OS is certainly an upgrade over Windows Server 2003 R2, it's not without it's flaws. Before you upgrade, learn some problems Windows admins might have with the new server and how to fix them.
Video: Author Mark Minasi dissects Windows Server 2008
While doing your own research on Windows Server 2008 is important, it also helps to hear what the experts think. In this exclusive interview, best-selling author Mark Minasi parses the best and worst of Microsoft's latest server OS and offers advice on Windows PowerShell, Group Policy and 64-bit computing.
Windows Server 2008 R2
In October 2009, Microsoft updated the OS with the launch of Windows Server 2008 R2, which includes a slew of new features and functionality. Learn more about getting started with R2.
PLANNING YOUR WINDOWS 2008 MIGRATION
So you've decided to move forward with Windows Server 2008 -- now the real work begins. This section goes through all the considerations that should be made during the planning process, including how to create a virtual Windows 2008 environment to help you become familiar with the OS before deployment.
Timing your migration to Windows Server 2008
Migrating to a new version of Windows comes with inherent risks. There are always undiscovered bugs in any software product. Over time, those bugs are flushed out and fixed. The later you migrate, the safer you are, but then you don't get the benefits of the new features either. Before planning your move to Windows Server 2008, first figure out which features in the new OS will save your organization money.
How a cost management analysis affects Windows Server 2008 migration
Calculating the financial gains and losses of a migration strategy can help you create a more cost-effective plan of action. Learn how to apply the principles of cost management analysis to your Windows Server 2008 planning strategy, and decide if the return of investment makes sense for you.
What to include in a Windows Server 2008 migration strategy
Once you're ready to move to the new network, you'll first have to put together a migration strategy. This book excerpt outlines the four major activities for migrating to Windows Server 2008: security principals, members servers, PCs and custom applications.
Building a Windows Server 2008 virtual test lab
When it comes to preparing for Windows Server 2008, there's nothing like hands-on experience, and the best way to get familiar with a new OS in to start using it in a practice setting. This tip explains the quirks of creating a test environment for Windows Server 2008 before your migration.
→ Configuring a virtual test lab on a budget
Not familiar with using virtualization as a testing/training tool? Learn the hardware and networking benefits of creating a virtual test environment, and how it can be a cost-effective way to ensure a successful Windows Server 2008 migration.
KEY WINDOWS 2008 FEATURES/IMPROVEMENTS
Windows Server 2008 features a number of management enhancements, including new additions like Server Manager and Server Core. This section reviews some of the most important new features for administrators, with details on how to get the most out of them.
Server Core
Server Core is a bare-bones installation option for computers running Windows Server 2008. While the installation results in less functionality, it also creates an environment that is easier to manage and maintain. In this article, learn how tools that Windows administrators can use to list and install Roles and Role Services make Server Core a popular Windows Server 2008 feature.
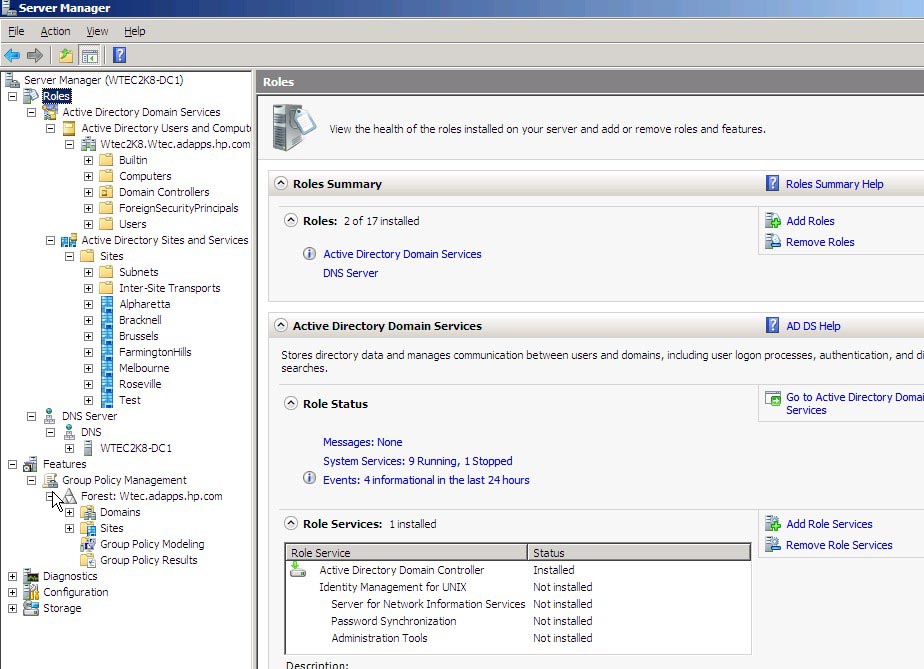
Server Manager
Integrating a central wizard-driven interface, Server Manager is a new feature in Windows Server 2008 that is designed to help IT departments tailor their servers just the way they want them. Here you can take a closer look at the role Server Manager plays in the OS.
→ A quick guide to Server Manager
Check out this crash course on everything Windows Server Manager has to offer, with a list of common administrative tasks and where to find them in Windows Server 2008.
Screenshot of the Server Manager console (Click to enlarge)
Group Policy
While working with Group Policy is nothing new for Windows admins, Windows Server 2008 provides faster searching and filtering than what was available in Windows 2003. Learn about the new wizard in Windows Server 2008's Group Policy Management Console, and how it enables searching and filtering on comments within settings with the Group Policy Object Editor.
Terminal Services
Changes to Terminal Services in Windows Server 2008 have resulted in improved support for knowledge workers needing support for multiple desktops, telecommuters and people working from remote offices. This article breaks down how and when these changes come into play.
→ TS Web Access simplifies application process
With Terminal Services Web Access in Windows 2008, the process of adding and removing applications can be as easy as clicking a checkbox. This tip breaks down the process for you.
Learn how RemoteApps in Windows Server 2008 gives Terminal Services administrators the ability to create a published desktop -- without the desktop.
Windows PowerShell
PowerShell is Microsoft's interactive command shell and scripting language, and it comes 'in the box' with Windows Server 2008. This learning center provides the basics to get you started with PowerShell scripting in Windows 2008, with details on what it is, how it works, and screencasts demonstrating basic commands.
P73-04755
More new features in Windows Server 2008 R2
Windows Server 2008 R2 comes equipped with several much-talked about features like Live Migration for Hyper-V and updates to Active Directory. But there are also quite a few notable features that have managed to fly under the radar. Learn more about the enhancements that make up R2.
CHANGES TO ACTIVE DIRECTORY
So much has been added to Active Directory in Windows Server 2008 that it easily deserves its own category. This section reviews some of the most important new Active Directory features for admins, such as the read-only domain controller and AD roles that are available with Server Core.
A first look inside the new features for Active Directory
This article provides an overview of some of the biggest changes made to Active Directory with the release of Windows Server 2008, with info on server roles such as Active Directory Domain Services and DNS.
Getting to know the read-only domain controller for Windows Server 2008
Perhaps the biggest addition to Active Directory for Windows 2008 involves the read-only domain controller (RODC). This article explains what 'read-only' means, and how the new feature can improve AD flexibility.
→ Video: Security benefits of the RODC
In this interview from Microsoft TechEd 2008, senior technical product manager Justin Graham explains how the RODC can help improve branch office security, while providing details on the app compaitibility considerations that admins should be aware of before deploying one.
Video: What else is new with Active Directory?
In addition to all the big and fancy features included with AD for Windows Server 2008, there are also a variety of 'lesser-known' changes that have been made. This video provides details on some of these improvements, such as stickiness prevention and fine-grained password policies.
Active Directory in Windows Server 2008 R2
Although Windows 2008 R1 included several improvements for Active Directory, key changes were made with R2, including a Recycle Bin feature and tweaks to Group Policy. Find more on key AD features in Windows Server 2008 R2.
Windows Server Hardware
VIRTUALIZATION WITH HYPER-V
Learning Windows Server 2008 R2
Hyper-V for Windows Server 2008 is a major landmark for Microsoft in terms of the company's standing in the server virtualization market. It's so big, in fact, that we gave it it's own page. Check out the link below to find answers to some of your burning Hyper-V questions.
Microsoft Hyper-V management for Windows 2008
This guide provides tips, book excerpts and video presentations to help give Windows administrators a better understanding of Microsoft's virtualization technology.
Diagram of Hyper-V's new hardware-sharing architecture (Click to enlarge)
Microsoft Hyper-V R2
The initial version of Hyper-V prompted Microsoft to update its virtualization platform with the release of Hyper-V R2 in October 2010 -- so what does Hyper-V R2 have to offer?
WINDOWS SERVER 2008 SECURITY CONSIDERATIONS
Many strides were taken to make Windows Server 2008 a more secure operating system than its predecessors. This section takes a look at some of these enhancements, and provides advice on how admins can further harden there servers in certain areas.
Network Access Protection: Should you care?
While NAP might not be as flashy as some of Windows Server 2008's other new features, admins shouldn't overlook the security benefits it has to offer. This article breaks down how NAP works in the operating system.
→ Simple NAP implementation
The installation process for Network Access Protection with Windows 2008 is easier than you think. Learn the basics of implementing NAP in your environment.
Security concerns with Server Core
Some of the lost functionality that goes with Server Core installations can make the OS a bit more difficult to properly secure. Follow these steps to ensure peak security when running Server Core, with advice on anti-malware, patching and command-line tools.
Windows PowerShell: A backdoor to malware?
One of the key benefits of Windows Server 2008 is that is comes with Windows PowerShell built in. However, if configured incorrectly this boon can quickly become a security liability. This tip explains how to avoid turning PowerShell into an entry point for malware.
Security in Windows Server 2008 R2
Security is often a top concern for admins moving to a new or updated operating system. Find out how Windows Server 2008 R2 beefs up protection.
Windows Server 2008 Web Edition
STORAGE IMPROVEMENTS WITH WINDOWS 2008
Many features were added to Windows Server 2008 in the area of storage management. Here you'll learn about some of these changes, including how SAN management has improved and exactly what happened to the NTBackup tool.
Windows Server Backup: The new NTBackup tool
Microsoft completely revamped its NTBackup program for Windows Server 2008. Dubbed Windows Server Backup, the feature is completely different from earlier versions, and includes new additons such as backup support for DVDs and the use of Volume Copy Snapshot Services (VSS) to perform disk-to-disk backups, to name a few.
→ Windows Server 2008 backup tool improves disaster recovery
Business continuity also gets a boost from the Windows Server Backup tool. This article explains exactly how disaster recovery has been made simpler with Windows Server 2008.

Getting the most out of the new self-healing NTFS
While it's not perfect, the new self-healing NTFS in Windows Server 2008 has several benefits over past Windows file systems. Here you'll learn more about how to avoid data corruption with this new feature.
Windows Server 2008 Learning Pdf
A first look at Storage Explorer
Microsoft designed the Storage Explorer utility in Windows Server 2008 to help deal with a common issue for companies that need to keep better track of SAN resources. While Storage Explorer doesn't actually document your SAN, it will allow you to browse it and see exactly how SAN resources are connected to your network. This article explains how it works.
DFSR in Windows Server 2008
With the release of Windows Server 2008, administrators can use Distributed File System Replication (DFSR) for SYSVOL replication, meaning they no longer have to deal with the poorly implemented File Replication Service (FRS). The catch? A tricky migration process when upgrading from Windows Server 2003 to 2008.
Keep an eye on network disk space
It's quite common to find unauthorized file types stored on network servers, which can not only cause problems with your network, but also leave your company vulnerable to certain legal liabilities. You can use the Server Manager in Windows 2008 to easily prohibit users from saving unauthorized file on your network.
Windows Web Server 2008 R2
TABLE OF CONTENTS
- Getting started with Windows Server 2008
- Planning your Windows 2008 migration
- Key Windows 2008 features and improvements
- Changes to Active Directory
- Virtualization with Hyper-V
- Windows Server 2008 security considerations
- Storage improvements with Windows 2008
- Inside Windows Server 2008 R2